MPI-Start requirements and design
Requirements
The development of MPI-Start comes from the necessity of having a single interface to upper layers of middleware and users to run a MPI job in a heterogeneous environment like the grid.
With MPI-Start, new MPI implementations and new batch schedulers should be easily supported without modifications in the Grid middleware or the user job descriptions.
Apart from starting MPI jobs, MPI-Start should support "simple" file distribution for sites without a shared filesystem and provide support for the users to help manage their data and applications.
Design
Design Goals
MPI-Start has the following design goals:
- Portability
- . The program must be able to run under any supported operating system
- Modular and extensible
- . New MPI implementations and batch systems should be easy to add.
- Relocatable
- . Must be independent of absolute path, to adapt to different site configurations and allow remote "injection" of mpi-start along with the job
- "Remote" debugging features
- . Must provide extensive debugging information for resolving problems.
Architecure
MPI-Start is a set of scripts that ease the execution of MPI programs by using a unique and stable interface to the middleware. The scripts are written in a modular way: there is a core and around it there are different plug-ins as shown in following figure. Three main frameworks are defined in the MPI-Start architecture:
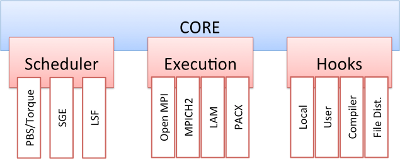
Scheduler framework. Every plug-in for this framework provides support for different Local Resource Management Systems (LRMS). They must detect the availability of a given scheduler and generate a list of machines that will be used for executing the application. The supported LRMSs are Grid Engine, PBS/Torque and LSF.
Execution framework. These plug-ins set the special parameters that are used to start the MPI implementation. It is not automatically detected, hence the user or workload management system must explicitly specify which MPI flavor will be used to execute the application. There are plug-ins implemented for Open MPI, MPICH2, MPICH, LAM-MPI and PACX-MPI.
- Hooks framework. In this framework any additional features that may be needed for the job execution is included. It is customizable by the end-user without the need of any special privileges. File distribution and compiler support is included in the hooks framework.
The hooks framework opens the possibility of customizing the behavior of MPI-Start. There are four classes of hooks: local-site, compiler, end-user, and file distribution. Local-site hooks allow the system administrator to set any configuration specific to the site that are not set automatically by MPI-Start. In order to obtain good performance and to assure that the binaries will fit the available resources, MPI jobs should be compiled with the local MPI implementation at each site. MPI-Start compiler support in the hooks framework detects the system architecture and sets the adequate compiler flags to build the binaries. Users can compile their application using the end-user hook, this is a shell script where the exact command line for building the application can be specified. Any input data preparation can be also done in that script.
One of the most important features in MPI-Start is the file distribution hook. Most MPI implementations need application binaries to exist in all the machines involved in the execution. This hook is executed once all the previous hooks have finished correctly and assures that all the needed files are available for the job at the different hosts. Prior to file distribution, a test detects the availability of a network file system. If this kind of file system is not found, MPI-Start will copy the files using the most appropriate method according to the site configuration. In the current implementation, the following methods are supported: OSC Mpiexec, ssh, mpi-mt (a MPI tool for copying files with MPI-IO) and copying the files to a shared area defined by the administrator.
The next figure shows the flow of execution of MPI-Start. The first step is the detection of the scheduler plug-in and the creation of a machinefile with the list of hosts in a default format. This is done automatically by checking the execution environment of the job.
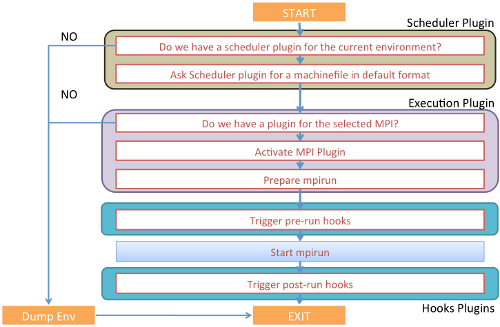
The next step is the selection of the execution plug-in according to the value specified by the user. The plug-in will activate the MPI implementation and prepare the correct command line to start the job. MPI-Start is able to detect any special tools available in the site, such as OSC Mpiexec, that may be used for a better startup of the application. If any of the two first steps fail, the program will exit and dump the execution environment to aid in debugging the problem.
Once the environment is ready to execute the MPI type selected, the hooks framework is executed in the following order: compiler, local-site, end-user and file distribution. If any of the hooks is not found it will be skipped. The following step is the actual execution of the application using the appropriate command line created by the execution plug-in and potentially modified by the hooks. The last step is the post-run hooks that allow fetching results or output processing. The post-run hooks executed are local-site, end-user and file distribution.
MPI-Start is implemented in a way that is easy to use even if it is not installed with special privileges. It can be included with the input files of the job and be executed from any location of the file system. The use of shell scripts for its implementation gives to MPI-Start good portability across systems. It also includes exhaustive debugging features. With different levels of debugging verbosity, MPI-Start can give from a totally silent output to a complete trace of all the steps performed during its execution.
